- Signs Your Earwax Buildup Needs Professional Attention - May 29, 2025
- A Step-by-Step Look at How Hearing Aids Make Sounds Sharper - May 5, 2025
- Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss? - April 27, 2025
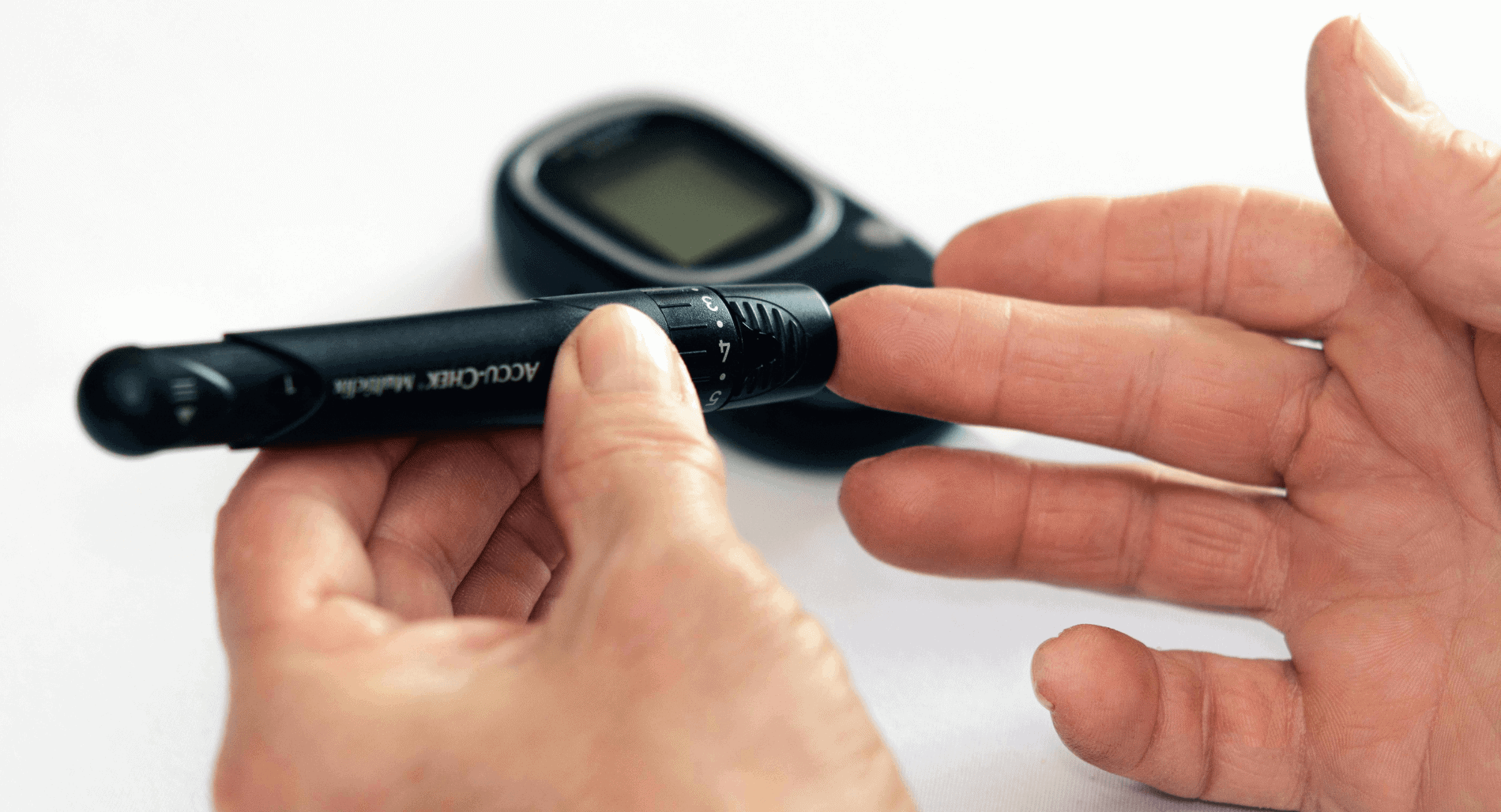
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While many are aware of its impact on blood sugar levels, few realize that diabetes can also affect hearing. Understanding the connection between diabetes and hearing loss, and taking proactive steps to monitor and manage this risk, is crucial for maintaining overall health.
The Connection Between Diabetes and Hearing Loss
Research has shown that individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience hearing loss compared to those without the condition. High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the small blood vessels and nerves in the inner ear, leading to hearing impairment. This damage can occur gradually and may go unnoticed until it significantly affects daily life.
Moreover, diabetes-related complications such as high blood pressure and heart disease can further increase the risk of hearing loss. Therefore, it is essential for individuals with diabetes to be vigilant about their hearing health and take steps to protect it.
Recognizing the Signs of Hearing Loss
Early detection of hearing loss is key to managing it effectively. Individuals with diabetes should be aware of the common signs of hearing loss, which include:
- Difficulty understanding conversations, especially in noisy environments
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves
- Turning up the volume on electronic devices higher than usual
- Struggling to hear high-pitched sounds, such as the voices of women and children
- Experiencing ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus)
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek a professional evaluation to determine if hearing loss is present and to what extent.
The Importance of Regular Hearing Health Exams
For those with diabetes, regular hearing health exams are crucial. These exams help detect any changes in hearing ability early, allowing for timely intervention and management. During a hearing health exam, a provider will conduct various tests to assess your hearing. These tests typically include:
- Pure-tone audiometry: Measures your ability to hear sounds at different pitches and volumes.
- Speech audiometry: Assesses your ability to hear and understand speech.
- Tympanometry: Evaluates the condition of the middle ear and eardrum.
Regular hearing health exams should be part of your overall diabetes management plan. Discuss with your healthcare provider how often you should schedule these exams based on your individual health needs.
Managing Hearing Loss
If a hearing health exam reveals hearing loss, there are several management options available. The most common treatment is the use of hearing aids. Modern hearing aids are highly effective and come with various features such as noise reduction, directional microphones, and Bluetooth connectivity. Your provider will help you choose the best hearing aid based on your specific needs and lifestyle.
Other management options include:
- Assistive listening devices: Tools such as amplified telephones and personal FM systems can help you hear better in specific situations.
- Cochlear implants: For severe hearing loss, cochlear implants can provide a sense of sound by directly stimulating the auditory nerve.
- Communication strategies: Learning techniques such as lip reading and using visual cues can enhance your ability to communicate effectively.
Preventive Measures
While hearing loss associated with diabetes cannot be entirely prevented, certain measures can help protect your hearing and slow its progression. Here are some tips:
- Maintain good blood sugar control: Keeping your blood sugar levels within the recommended range can reduce the risk of damage to the blood vessels and nerves in the inner ear.
- Protect your ears from loud noises: Use earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments to prevent additional damage to your hearing.
- Avoid ototoxic medications: Some medications can harm your hearing. Discuss with your healthcare provider any potential risks and alternatives.
- Stay physically active and maintain a healthy diet: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can improve your overall health and hearing.
The Role of Support
Managing both diabetes and hearing loss can be challenging, but support is available. Joining support groups for individuals with diabetes or hearing loss can provide valuable information, resources, and emotional support. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can help you navigate the challenges and find effective solutions.
Monitoring hearing loss is essential for individuals with diabetes. Recognizing the signs, scheduling regular hearing health exams, and managing any detected hearing loss can significantly improve your quality of life. By taking preventive measures and seeking professional support, you can protect your hearing and maintain overall well-being. Remember, proactive steps today can lead to better hearing health tomorrow.
